Before comparing SQL Server databases, you will need to add them to the workspace. The "Add Databases" functionality can be accessed from the ribbon (the "Home" tab) or from the "Add Databases" action link located in the top-left section of the Workspace.
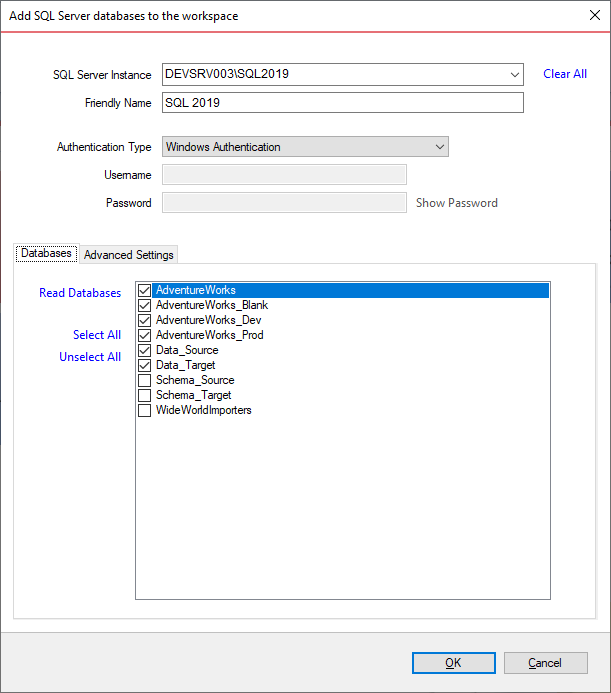
On the "Add Database" window, enter the SQL Server instance, a friendly name you wish to use in the UI and the SQL Server credentials. You can click on the "Refresh" item of the SQL Server drop down to discover the SQL Server instances running on your network. If the application is not able to discover SQL Server instances, type in the SQL Server instance in the drop down box.
 |
If the SQL Server is not listening on the default port 1433, you can specify the port number as: [ServerName]\[Instance Name],PortNumber |
Data comparison supports four types of authentication:
- Windows Authentication
- SQL Server Authentication
- Azure Active Directory Integrated Authentication
- Azure Active Directory Password Authentication
 |
The Azure Active Directory Authentication requires a component named Microsoft Active Directory Authentication Library for SQL Server. The comparison tools will display a warning message when Azure Authentication is selected for a SQL Server and this library is not found. The setup checks for it during the installation as well and recommends installing it if the component is missing. You can download this library from Microsoft at: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=48742 |
Once you have chosen the SQL Server and the credentials, click on the "Read Databases" link. Data compare will connect to the specified SQL Server and bring in the databases from that server. You can add one or more databases to the workspace by checking them in the database listbox.
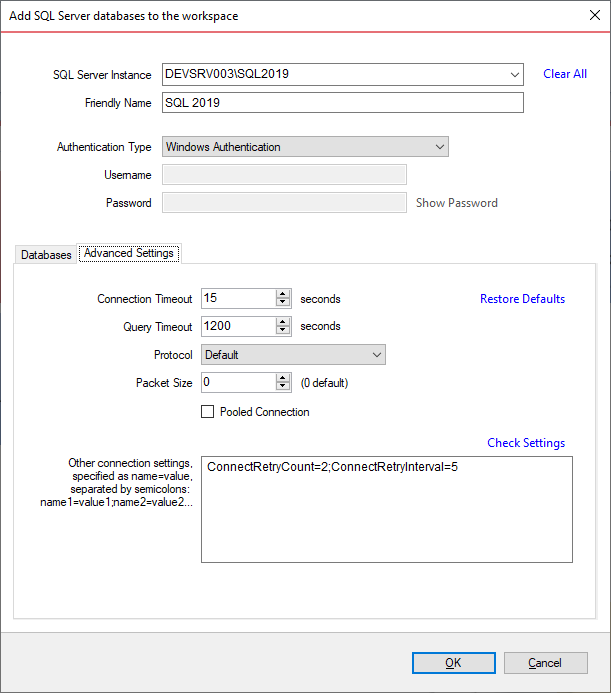
Under the "Advanced Settings" tab, you can enter various connection settings, such as the timeouts, the connection protocol, packet size and a few more. By default data compare uses the advanced settings specified in the Application Settings.
The "Other connection settings" edit box, allows to specify additional connection properties as name=value, separated by semicolons: name1=value1;name2=value2;... To check whether these properties are allowed for a SQL Server connection, click on the link "Check Settings". For a full list of the connection properties supported for by a SQL Server database, check the MSDN.
The following property names are already included in the SQL Server connection and should not be specified in the "Other connection settings". Their synonyms must be excluded as well:
- Data Source
- Initial Catalog
- Integrated Security
- Persist Security Info
- User ID
- Password
- Pooling
- Connect Timeout
- Network Library
- Packet Size
- Application Name
- Authentication